Rapid Prototyping Services With XMAKE
XMAKE offers rapid prototyping services, transforming ideas into tangible products swiftly. Our digital platform ensures fast, cost-effective, and high-quality model production, accelerating your design-to-market process.
- Create Prototypes in 24 Hours
- Up to 0.01mm Resolution
- 50+ Materials Options
- Fast Turnaround
- High-Quality Resolution
- Material Versatility
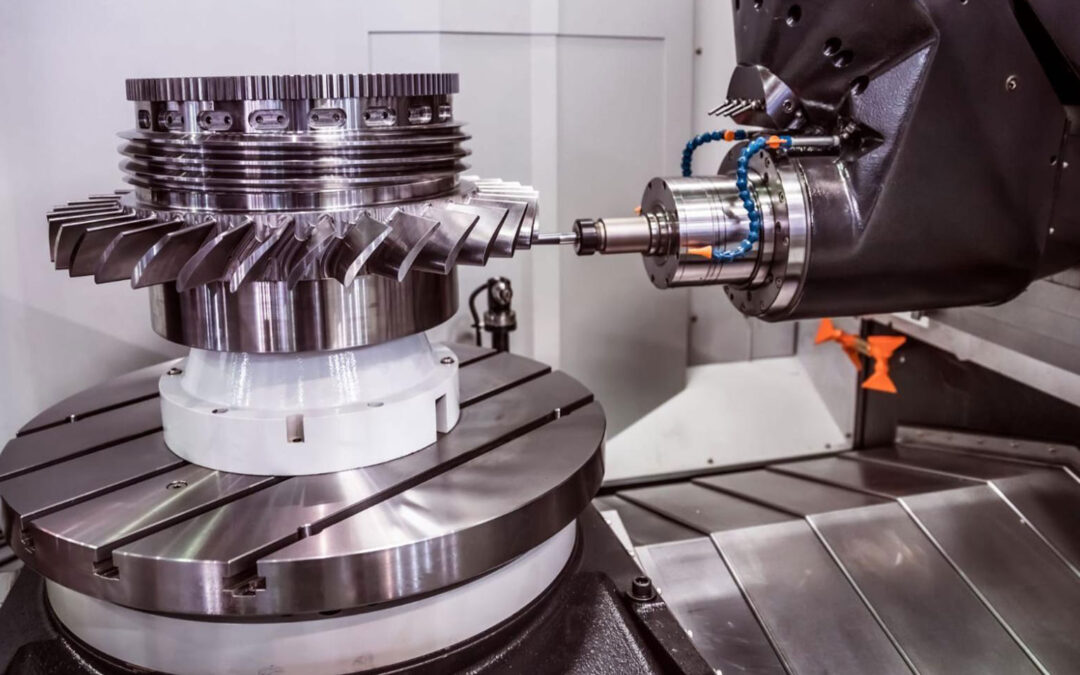
Rapid Prototyping Processes at XMAKE
Rapid Prototyping Materials Selection
Metal Materials

Aluminum
Aluminum's conductivity and strength-to-weight ratio make it ideal for 3D printing and rapid prototyping of structural components.

Carbon Steel
With balanced mechanical properties, carbon steel is key for rapid prototyping of high-strength moving parts like turbine blades.

Stainless Steel
Prized for corrosion resistance, stainless steel is used in rapid prototyping for vehicle structures and aircraft parts.
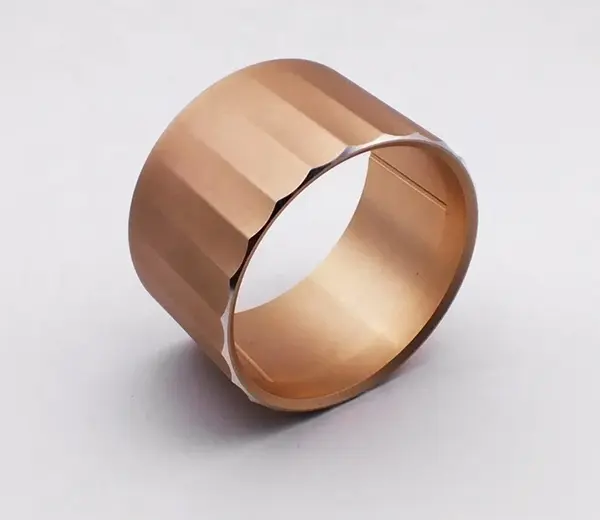

Copper
Known for conductivity, copper in rapid prototyping often makes electronic wires and heat sinks for devices.
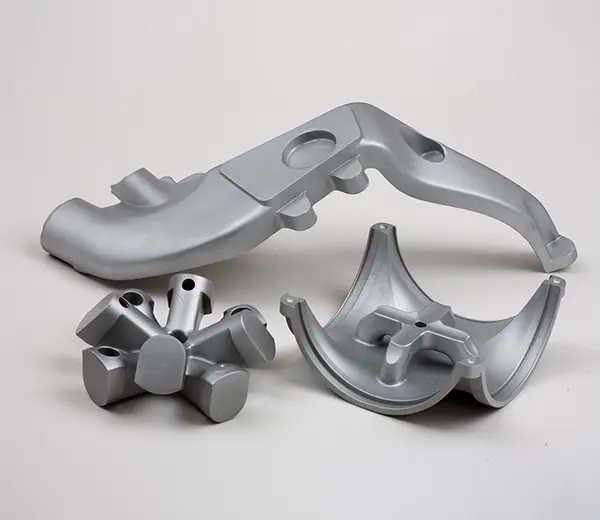

Magnesium Alloy
Superior corrosion resistance makes magnesium alloy suitable for automotive and construction parts in rapid prototyping.
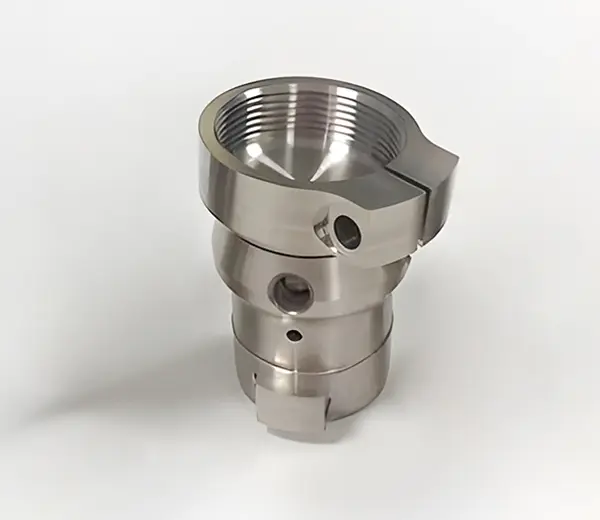

Titanium Alloy
This light, strong material with good biocompatibility is processed via SLS or SLM for complex, lightweight metal parts in rapid prototyping.
Plastic Materials
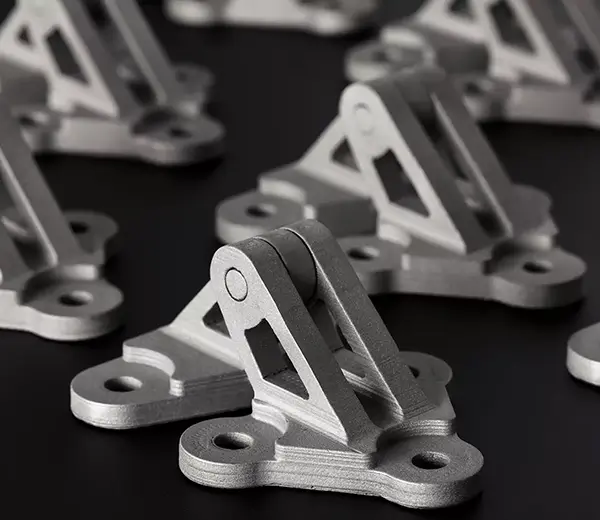

PLA (Polylactic Acid)
PLA is a biodegradable plastic, commonly used in desktop 3D printers, favored for its eco-friendly properties.
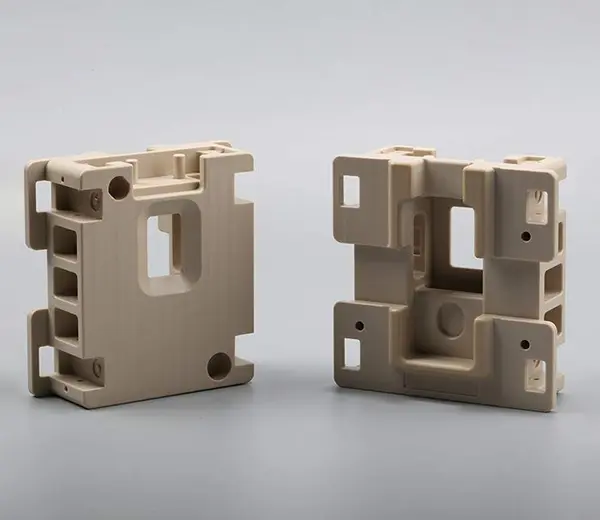

ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
ABS is a standard FDM printing material, known for its mechanical strength and heat resistance, suitable for complex structural parts.

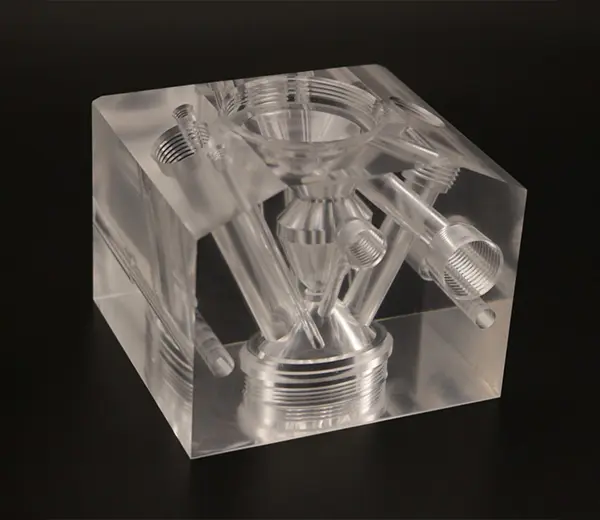
PA (Nylon)
Nylon offers excellent wear and chemical resistance, ideal for manufacturing wear-resistant components and mechanical parts.

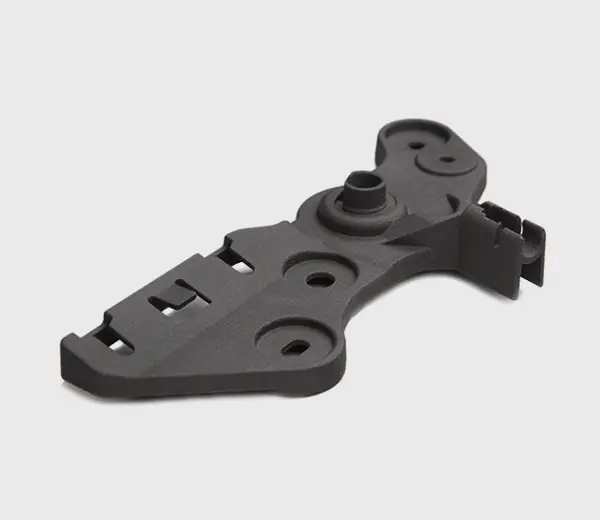
PC (Polycarbonate)
PC is a high-strength, heat-resistant plastic, used for products like eyeglass lenses, compact discs, and bulletproof glass.
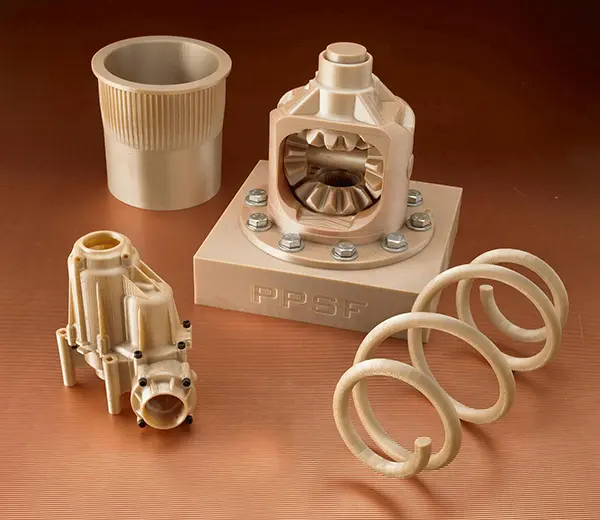

PPSF (Polyphenylsulfone)
PPSF (also known as PPSU) exhibits extreme strength and heat resistance, suitable for high-end industrial applications such as aerospace and medical devices.

ULTEM (Polyetherimide)
ULTEM is a high-performance plastic with superior mechanical properties and heat resistance, used in electronics, electrical, and aerospace industries.
- We can source any other material on request, but quotes take up to 48 hours.
Rapid Prototyping Steps at XMAKE

Upload File
Start by uploading your CAD files securely to our platform.

Design Feedback
Receive expert feedback to optimize your designs for manufacturing.

Rapid Prototype
Quickly turn designs into prototypes with state-of-the-art technology.

Premium Quality
Guaranteed high-quality production, ISO 9001:2018 certified for excellence.

24/7 Supported Guidance
Experience continuous support and guidance throughout the manufacturing process.
Precision Rapid Prototyping for Diverse Industries
Robotics
Aerospace
Automotive
Consumer Products
Medical Devices
Why Choose XMAKE’s Custom Rapid Prototyping Services

Advanced Technology and Equipment

Speed and Efficiency

Customization and Expert Consultation
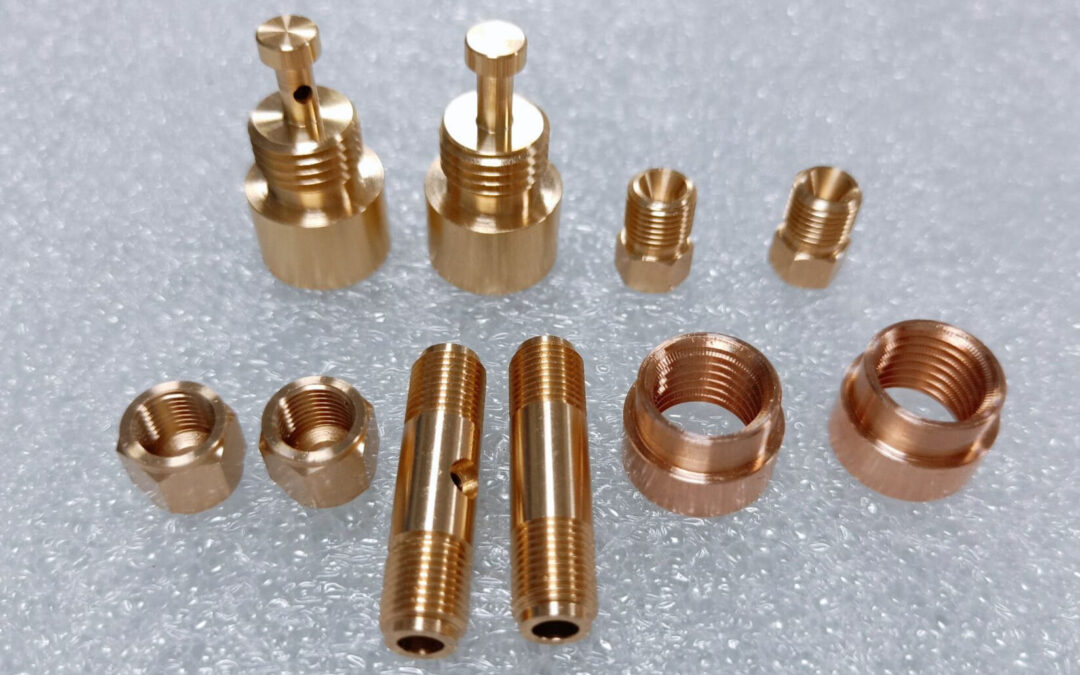
High-Quality Rapid Prototyping Parts Made By XMAKE
XMAKE Customer Success: Solving Challenges Together

Unmatched Prototyping Speed
“XMAKE’s rapid prototyping services have dramatically reduced our product development time. The speed and efficiency with which they work are truly unmatched, allowing us to bring innovative ideas to life faster than ever before.”
Sarah Lin
Product Development Manager at InnovateTech

Precision and Reliability
“We have been consistently impressed by the precision and reliability of XMAKE’s prototyping services. Their attention to detail and commitment to quality have made them our go-to partner for all our prototyping needs.”
Tom Fischer
Chief Design Officer at DesignForward Inc.

Seamless Customization Experience
“XMAKE’s ability to offer seamless customization for our prototypes has been a game-changer. Their team works closely with us to understand our vision and delivers prototypes that perfectly match our design requirements.”
Dr. Evan Zhang
Director of Product Innovation at NextGen Solutions
Rapid Prototyping FAQs
1. When do I need rapid prototypes?
There are a couple of scenarios where rapid prototypes become a need. The first is when the cost of product development becomes too high. Rapid prototyping cost is lower than conventional prototyping, reducing product development costs. Rapid prototypes are also needed when you need to identify and evaluate product hazards as well as test functionality.
2. Is rapid prototyping different from 3D printing?
Rapid prototyping and 3D printing are completely different from each other. 3D printing is a technology that uses additive manufacturing to develop products. On the other hand, rapid prototyping is an umbrella term for a group of techniques used for the manufacturing of product parts from a 3D CAD model.
3. What materials can be used in rapid prototyping?
Materials vary depending on the technique used and can include plastics, resins, metals, ceramics, and composite materials. Each material has specific properties suited for different applications.
4. What is the difference between rapid prototyping and traditional prototyping?
Making design modifications after the CNC machining process has started can be complex and may incur additional costs and lead time. It's best to finalize the design before the process begins. However, if necessary, we can work with clients to make changes, understanding that it may affect the project timeline and cost.
5. What industries use rapid prototyping?
Rapid prototyping enables quick validation of design concepts, functional testing, and iterative improvements. It accelerates the development process, reduces costs, and enhances innovation by allowing designers to experiment and refine their ideas before committing to mass production.
6. Can rapid prototyping be used for production parts?
Yes, in some cases, especially with advances in 3D printing technologies, rapid prototyping can be used for small-batch production or custom parts. However, for large-scale production, traditional manufacturing methods are still more economical.
Looking for Online Rapid Prototyping Services?
-
All uploads are secure and confidential.
All uploads are secure and confidential.
Learn More about Rapid Prototyping Resources
Can You 3D Print Metal?
Can you 3D print metal? Explore the materials, methods, pros and cons, and home vs. industrial options for metal 3D printing. Learn which metals work best and how to get started.
Tin Metal: Definition, Composition, Alloys and Uses
Explore the properties, composition, and uses of tin metal and tin bronze, including QSn6‑6‑3, and learn how these materials are ideal for durable, CNC-machined components.
Understanding Anodized Aluminum
Discover how anodized aluminum enhances durability, corrosion resistance & aesthetics. Learn types, uses & limitations. Expert insights from xmake.
All About Austenitic Stainless Steel
Learn the properties, grades, applications, and benefits of austenitic stainless steel, especially 300 series, and how Xmake’s CNC services deliver precision parts.
What Is Brass Made Of: A Comprehensive Guide!
Brass is a metal alloy mainly made of copper (55–95%) and zinc (5–45%), with minor elements added to enhance its properties and versatility.
What is CNC Milling: An Ultimate Guide!
Explore what CNC milling is, how a CNC mill works, and key features of a milling machine with CNC control in this complete guide.
How to Choose Reliable CNC Machining Services?
Learn how to choose CNC machining services wisely. Compare equipment, certifications, precision & materials for optimal results. Get quality parts on time.
Resin vs Plastic: Here is the Difference
Wondering is resin plastic? Learn the key differences between resin and plastic, their uses, and when to choose each for your projects.
Nut vs Bolt: What is the Difference?
Explore the essential differences in nut vs bolt, including their types, materials, and best applications. Learn how to choose and maintain the right fasteners for your needs.
CNC Plasma Cutter: How It Works, Benefits & Selection Tips
Explore how a CNC Plasma Cutter cuts metal with precision. Learn key benefits, speed, thickness capacity, tolerance and how to choose the right system.