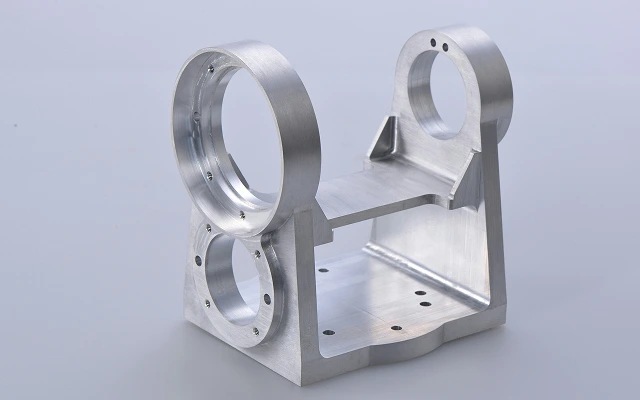
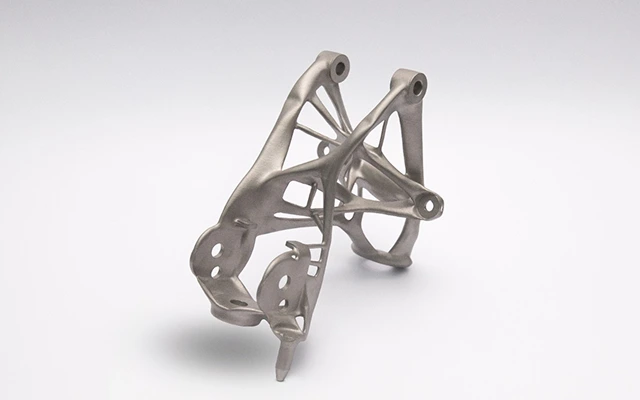
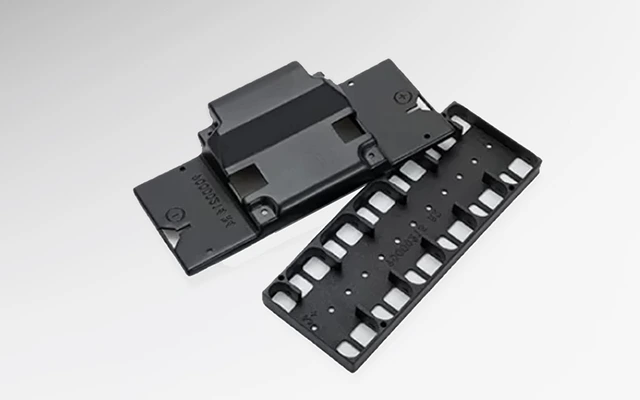
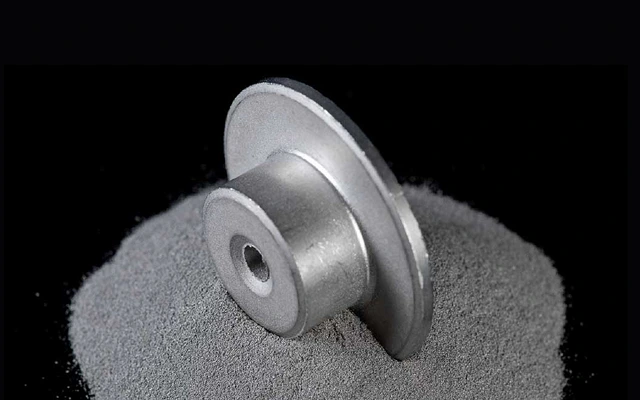
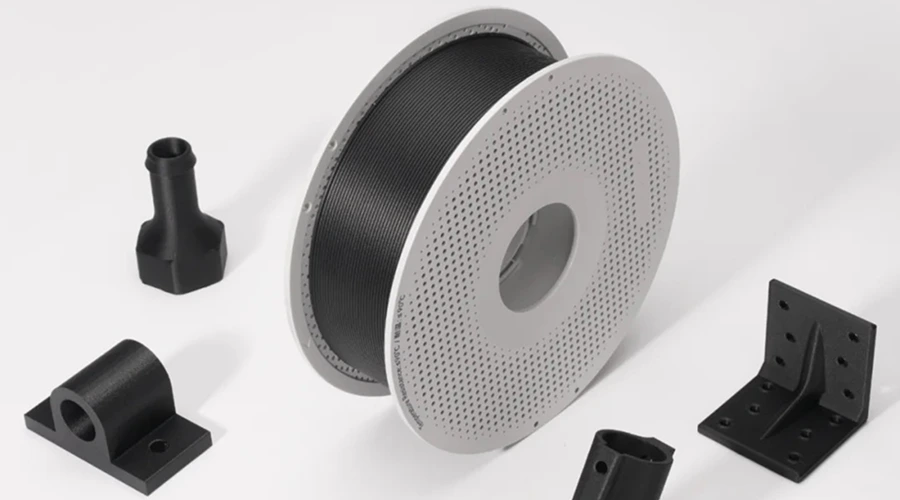
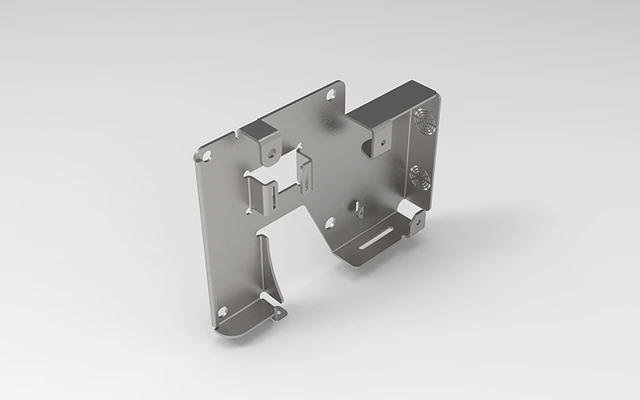
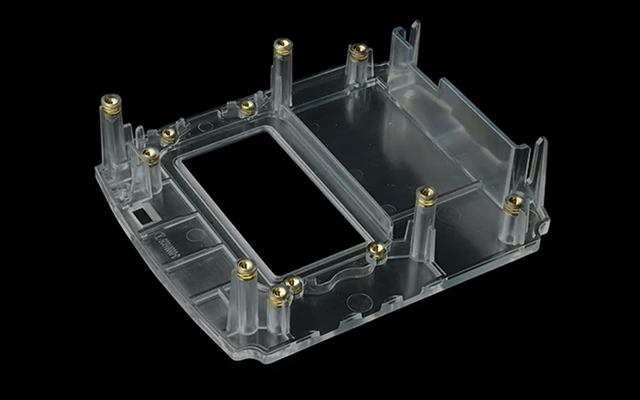
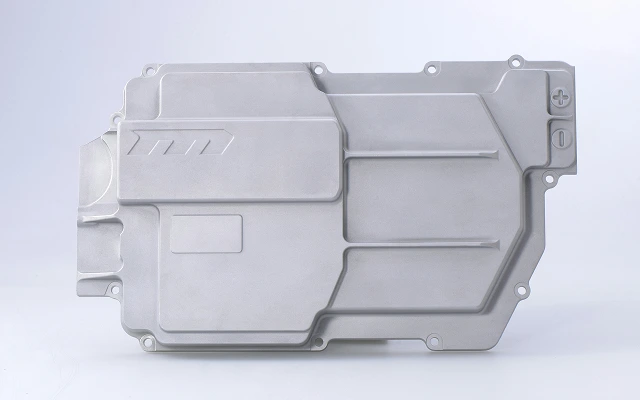
Robotics parts manufacturing solutions, customize your Robotics parts
Expert robotics components manufacturer. We deliver precision-engineered parts meeting the highest industry certifications. We've supplied mission-critical components for 120+ robotics companies and 300+ robot models with flawless performance. We continuously optimize manufacturing efficiency and cost structures, enabling you to deploy advanced robotic systems economically.