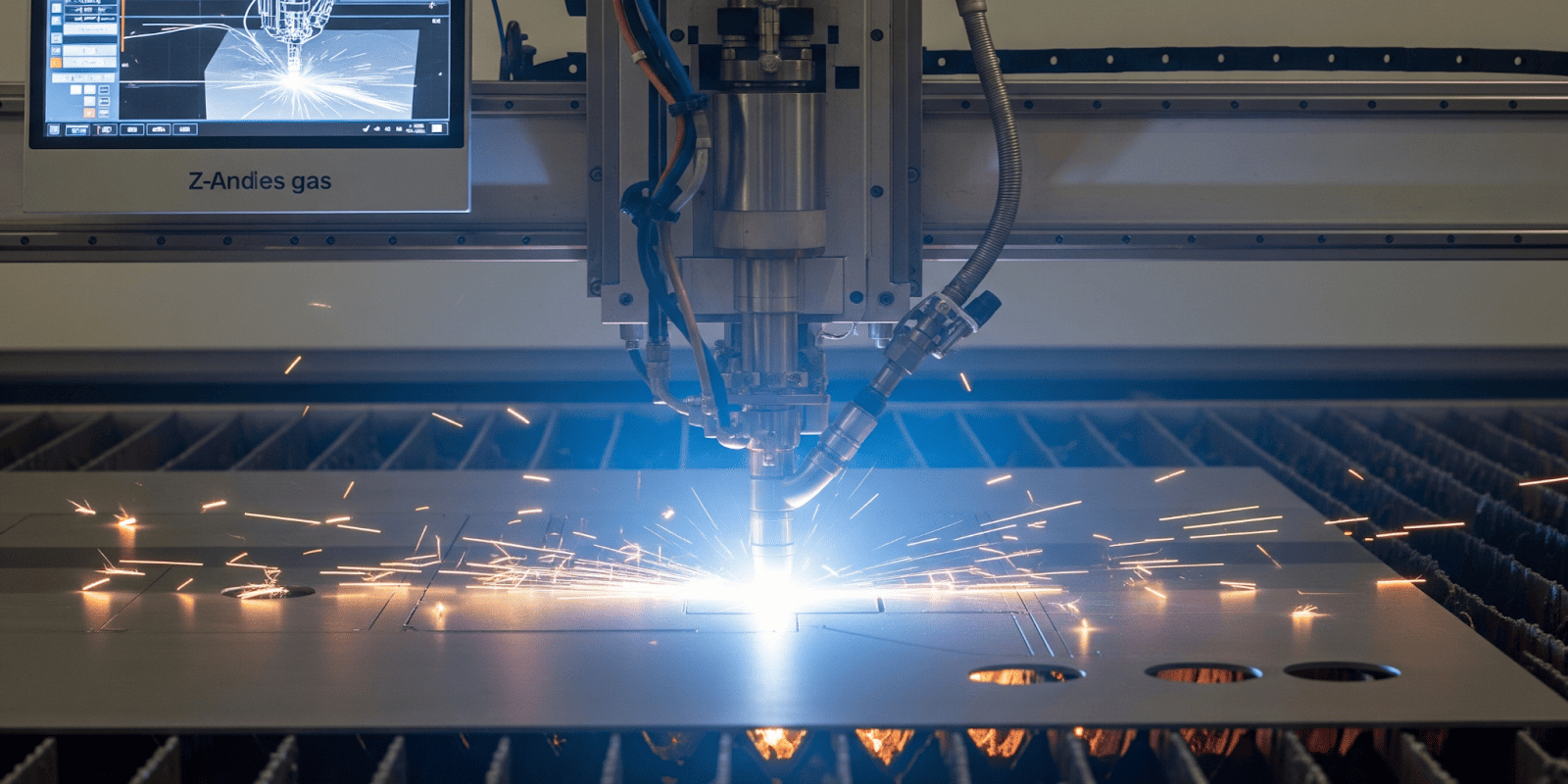
CNC plasma cutting is a high-precision metal fabrication process that combines computer numerical control (CNC) with plasma arc technology to cut electrically conductive materials. This method is widely used in industrial manufacturing, custom metalwork, and prototype development for its balance of speed, cost-efficiency, and versatility.
This guide explains how a CNC plasma cutter works. You’ll discover its advantages over lasers or oxy-fuel systems. Learn to choose the right machine for your shop’s needs.
How Does CNC Plasma Cutter Work?
The plasma cutter operates through the coordination of several key components:
- a plasma torch
- a power supply
- a CNC controller
- a motion system (such as a gantry or robotic arm)
The CNC controller interprets digital design files (like DXF or G-code) and guides the torch’s movement along precise paths. The power supply generates the electrical energy needed to create the plasma arc, while the torch directs this arc toward the workpiece. Together, these elements allow for automated, highly accurate cutting.
The cutting process begins when the plasma arc is formed between an electrode inside the torch and the metal surface. As the compressed gas passes through the arc, it becomes superheated and ionized, transforming into plasma.
This plasma jet reaches temperatures above 25,000°C (45,032°F), instantly melting the metal. Simultaneously, the high-pressure gas stream blows away the molten material, producing a clean, narrow cut. CNC plasma cutting is especially effective on mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, typically in thicknesses ranging from 1 mm to 50 mm.
- Cutting Table Types
Cutting tables support materials during processing. Water tables submerge workpieces underwater. This reduces noise by 20 decibels and traps fumes. Downdraft tables use suction systems. They pull smoke downward through filters. Water tables suit high-production shops. Downdraft systems allow dry cutting. Both protect operators from hazards. Table choice impacts cut quality and safety.
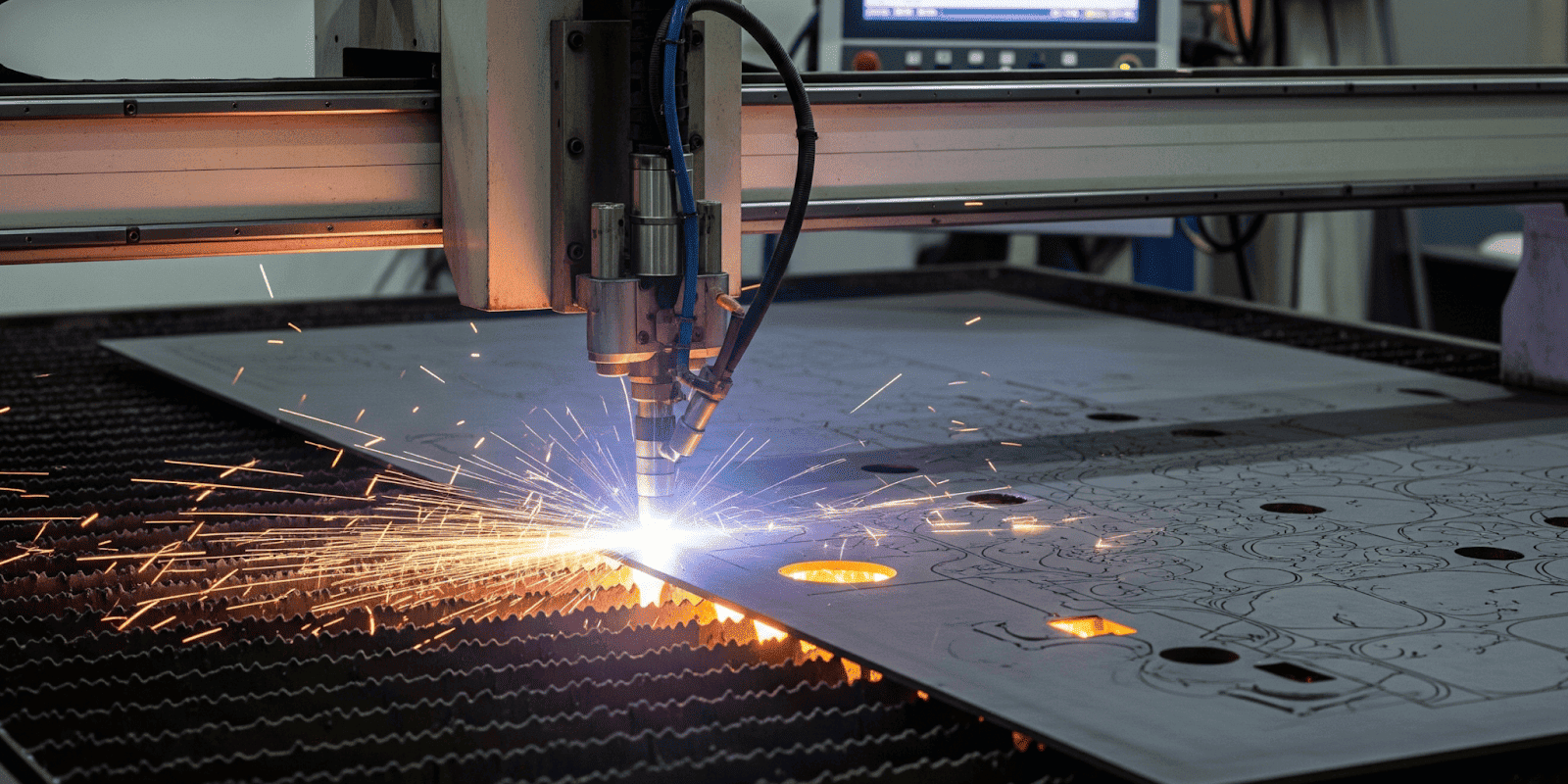

CNC Plasma Cutting Materials
Plasma cutting requires electrically conductive workpieces. Non-conductive materials cannot complete the electrical circuit. Plasma cutting is suitable for a wide range of electrically conductive metals.
Its ability to handle different material types and thicknesses makes it a preferred method in industries such as construction, automotive, and metal fabrication. Below are the most commonly used materials:
- Mild Steel – The most common material for plasma cutting due to its excellent conductivity and affordability. Cuts are fast and clean, especially for structural components.
- Stainless Steel – Offers good cut quality, though heat-affected zones may require post-processing depending on precision requirements.
- Aluminum – Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, aluminum cuts well with plasma, though it requires careful control to avoid dross formation.
- Galvanized Steel – Can be cut effectively, but the zinc coating produces fumes, so proper ventilation or fume extraction is necessary.
- Copper and Brass – These highly conductive metals can be plasma cut, but often require specialized settings to manage thermal conductivity and reflectivity.
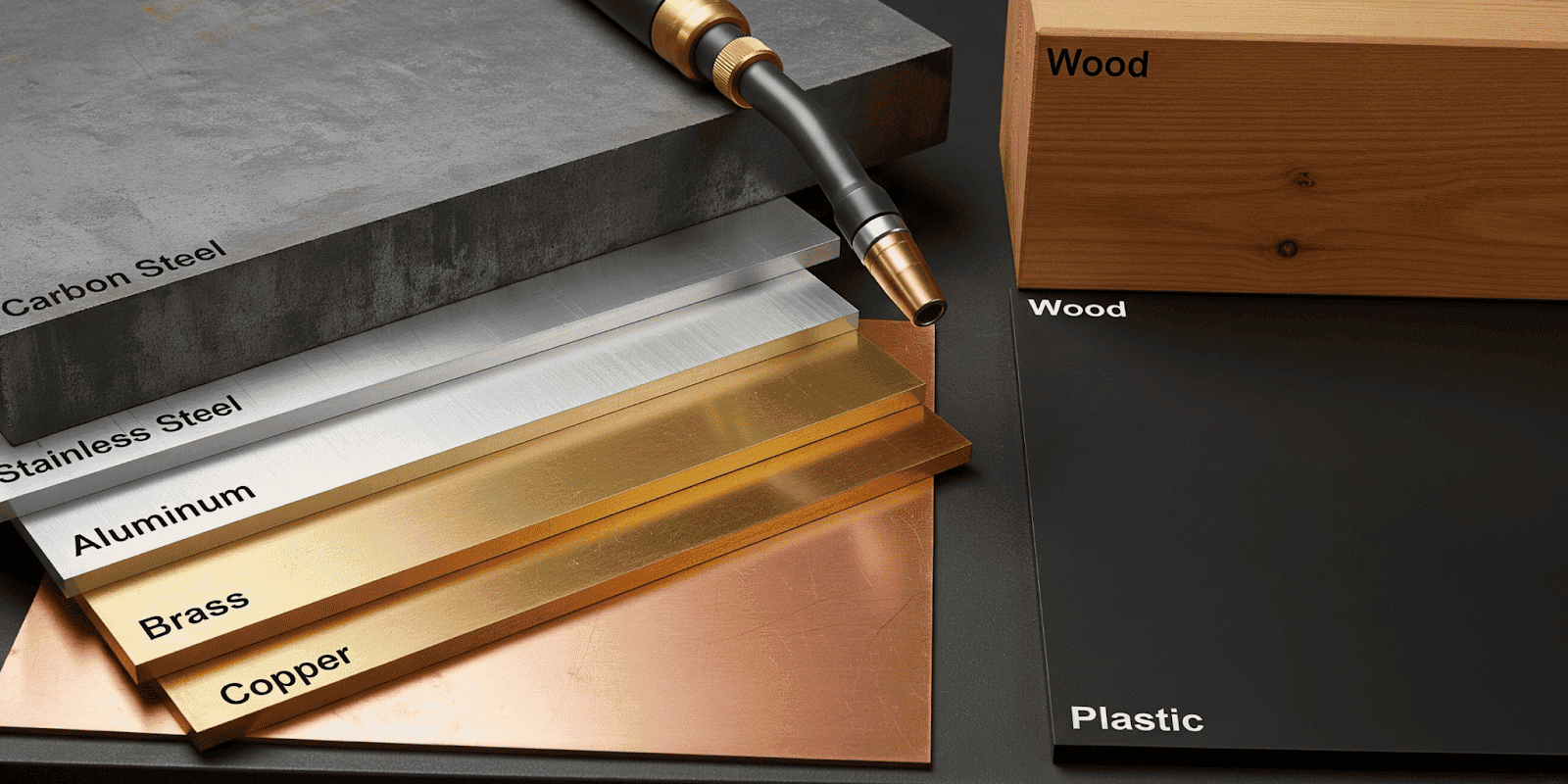

Image: cnc machining materials
Advantages of CNC Plasma Cutting
The integrated components enable significant operational benefits. These advantages make CNC Plasma Cutting preferred for industrial applications.
Precision
With computer-controlled motion, CNC plasma systems can produce consistent, accurate cuts, even on complex geometries. Once a design is programmed, it can be replicated with minimal deviation, which is critical for batch production or parts requiring tight tolerances.
High Cutting Speed
CNC plasma cutters can move the torch rapidly across the workpiece, making them significantly faster than traditional cutting methods, especially for medium-thickness metals. This reduces cycle times and boosts overall productivity in manufacturing and fabrication.
Cost-Effective
CNC plasma cutting is up to 10 times faster than oxy-fuel cutting for medium-thickness steel, cutting a ½-inch plate in under a minute versus several minutes. It also uses compressed air instead of costly gases like acetylene, reducing operational costs.
Compared to lasers, plasma systems are more affordable and efficient for many industrial applications, improving overall shop profitability.
Compared to laser or waterjet cutting, plasma cutting offers a more affordable solution for materials like mild steel in the 1–25 mm range. It balances precision with speed, making it ideal for projects that don’t demand ultra-fine finishes.
Versatile Material Compatibility
CNC plasma cutters handle a broad range of conductive metals, from steel and stainless to aluminum and copper alloys. This flexibility supports diverse industrial needs, from structural work to detailed metal art.
Integration with CAD/CAM Workflows
These machines accept digital design files and integrate seamlessly with CAD/CAM software, simplifying the transition from concept to finished part. This also reduces the chance of human error during setup and cutting.
Applications for CNC Plasma Cutter
CNC plasma cutting is widely adopted across industries that require fast, accurate, and cost-effective metal processing. Its ability to handle various metals and part geometries makes it a versatile solution for both high-volume production and custom fabrication. For example:
- Industrial Fabrication: Used to cut structural steel components like I-beams, brackets, and conveyor parts with precision, reducing post-weld adjustments and improving production speed.
- Automotive: Ideal for cutting chassis components, frame rails, and suspension mounts. Enables efficient fabrication of parts like exhaust manifolds with clean, repeatable cuts.
- Aerospace: Supports high-precision cutting of aluminum and stainless components such as wing ribs and turbine housings, maintaining tolerance and structural integrity in lightweight designs.
- Construction: Used on-site or in prefab facilities to cut steel plates, beams, and panels for buildings, bridges, and infrastructure projects.
- Agricultural Equipment: Cuts parts for tractors, harvesters, and implements, where robust, large-format metal parts are common and production volume is moderate to high.
- Signage and Decorative Metalwork: Enables detailed cutting of custom signs, panels, and art pieces from aluminum or steel with design-driven precision.
- Prototyping and Job Shops: Offers quick turnaround for one-off or low-volume parts, helping businesses iterate and deliver parts without long lead times.
Choosing the Right CNC Plasma Cutter
Selecting the right CNC plasma cutter depends on your specific application needs, including material type, production volume, and required precision. While all cnc machines operate on the same basic principle, their capabilities can vary significantly based on power output, table size, and control features. Key factors to consider:
- Material type and thickness
- Cutting speed requirements
- Table size and work area
- Power supply capacity (amperage)
- CNC controller and software compatibility
- Type of plasma torch (air-cooled or water-cooled)
- Ventilation or fume extraction systems
- Level of automation and ease of use
- Budget and maintenance costs
Choosing CNC Plasma Cutting Services
Not every business needs to invest in a CNC plasma cutter, especially when production demands fluctuate or equipment costs are prohibitive. In such cases, outsourcing to a reliable CNC plasma cutting service is a practical solution. Xmake offers professional CNC plasma cutting services directly from our own factory, ensuring precise fabrication with fast turnaround times.
Our streamlined cnc online quoting system allows you to upload designs and receive instant quotes, with no minimum order requirements. Whether you need prototype parts or mid-volume production, Xmake’s expertise and modern equipment guarantee quality results delivered promptly to your doorstep.
FAQs
Do plasma cutters use a lot of electricity?
Plasma cutters use electricity based on their power rating. Standard machines run around 200 amps for cutting up to 1.5 inches of steel, while industrial models exceed 400 amps for thicker materials.
Can a plasma cutter cut a car?
Yes, plasma cutters can cut automotive parts made from steel, aluminum, or other conductive metals. They are commonly used in auto body repair and fabrication to cut frames, panels, and exhaust components quickly and accurately.
What are some common mistakes made with plasma cutting?
Typical mistakes include using incorrect gas pressure, poor torch height control, improper cutting speed, and inadequate grounding. These issues can lead to rough cuts, excessive dross, or damage to the torch and workpiece.
How thick of steel can a CNC plasma cutter cut?
Most CNC plasma cutters can effectively cut steel up to 25 mm (1 inch) thick. With high-power systems, cutting thickness can reach 50 mm (2 inches) or more, but quality and speed may decrease at greater thicknesses.